Using Multiple Versions of R Concurrently
Determining Available Versions
RStudio Workbench scans for and automatically discovers versions of R in the following locations:
/usr/lib/R
/usr/lib64/R
/usr/local/lib/R
/usr/local/lib64/R
/opt/local/lib/R
/opt/local/lib64/R
/opt/R/*
/opt/local/R/*This is described in more detail in the Recommended Installation Directories section. If you have installed versions of R in alternate locations, you can list them within the /etc/rstudio/r-versions configuration file. For example:
# /etc/rstudio/r-versions
/opt/R-3.2.1
/opt/R-devel-3.3In addition, any version of R referenced in an r-version directive within User and Group Profiles is also recognized.
In order to be usable, the R home path must be readable by the RStudio server account (usually rstudio-server; see Access and Security for details).
Version Scan Report
At startup, RStudio Workbench collects information about each available R version as described above, and writes a report to the following file in JSON format:
/var/lib/rstudio-server/r-versionsThis file is later read by the various RStudio processes responsible for displaying and switching between R versions. If you aren’t seeing the R versions look and work as you expect, the content of this file can give you some insight into RStudio’s understanding of your system’s configuration. If you’re unable to resolve the issue, include the contents of the file when submitting a support ticket to support@rstudio.com.
Note that the JSON format of the r-versions file is subject to change between RStudio versions, so avoid reading or using it in automated tooling.
The r-versions file must be available on all nodes that run R sessions. We don’t generally recommend changing its location, but if you need to do so in order to mount it on R session nodes, you can do via the r-versions-path option as in the following example:
# /etc/rstudio/rserver.conf
r-versions-path=/mnt/config/rstudio-server/r-versionsExtended R Version Definitions
The /etc/rstudio/r-versions file allows you to specify extended information for a particular R Version, providing you:
- The ability to specify additional environment variables to set
- An optional preload script to run
- An optional environment module to load (more info here)
- A user-friendly label name for the version that is displayed in the UI
To specify extended format information, modify the /etc/rstudio/r-versions file to consist of multiple R entries separated by a blank line. The following table lists the fields that are available for each R entry in the file.
| Path | (Required if Module not specified, see Modules) The root directory of the location of the R installation. |
| Label | (Optional) The user-friendly name for the R version that will be displayed to users in the UI. |
| Module | (Optional) The name of an environment module to load for the R version. This is loaded by running the command module load [module] after sourcing the user’s .bashrc file. |
| Script | (Optional) A script to run once the environment has been loaded but before the session process has been launched. |
| Repo | (Optional) A string representing a CRAN Repository URL, or the path to a repos.conf file which lists multiple package repositories. See CRAN Repositories for more information. |
| Library | (Optional) A : separated list of directories which house the desired R packages for the particular R version. Overrides the R_LIBS_SITE environment variable. This will be combined with R_LIBS_USER when forming the R library paths. Most R installations use a default site library located at $R_HOME/site-library, so you may need to include the default site library path directories when setting this field. |
An example /etc/rstudio/r-versions file is shown below.
# /etc/rstudio/r-versions
Path: /opt/R/R-2.15.3
Label: My special R Version
Module: testmodule
Script: ~/rload.sh
Repo: https://cran.ms.unimelb.edu.au/
Library: /share/packages/R-2.15.3
Path: /opt/R/R-2.15.3-alternate
Label: My special R Version 2
Module: r/latest
Label: Latest version of R
/opt/misc/R/SpecialR1
/opt/misc/R/SpecialR2
/opt/mic/R/AltnerateRIt is important that each entry consists of the fields as specified above. Each field must go on its own line. There should be no empty lines between field definitions.
Each R entry must be separated by one full blank line (two new-line \n characters). If only the path is being specified, with no label, script, or module, you may simply list the path to the installation (as in previous versions). Paths are not separated by a blank line, but they must be separate from extended definitions by a blank line (as in the above example).
Modules
By setting the name of a module in an environment definition, that version of R will be loaded entirely by module. When a module is defined and the Path is not specified, the default R binary on the path will be used once the module is loaded. Otherwise, if Path is specified, that specific binary will be used.
If you do not specify a Path to the R installation, you must ensure that RStudio Workbench can load the module by specifying the location of the module shell initialization script for sh. For example:
# /etc/rstudio/rserver.conf
modules-bin-path=/usr/local/Modules/3.2.9/init/shFailure to do so will result in RStudio Workbench being unable to verify the version, which will cause it to be unavailable for use.
Reloading Configuration
In order for the changes to the /etc/rstudio/r-versions file to be detected, you must either restart RStudio (via sudo rstudio-server restart) or send the SIGHUP message to the rserver process. This can be done using kill -s SIGHUP to the server process, or via the reload command:
sudo rstudio-server reloadExcluding Versions
If you have versions of R on your system that would normally be picked up by automatic scanning but which you’d like to exclude, the most straightforward thing to do is to disable R version scanning altogether and explicitly specify all versions you’d like to use in /etc/rstudio/r-versions. For example:
# /etc/rstudio/rserver.conf
r-versions-scan=0Switching Between Versions
To switch between versions of R you use the version menu near the top right of the IDE:
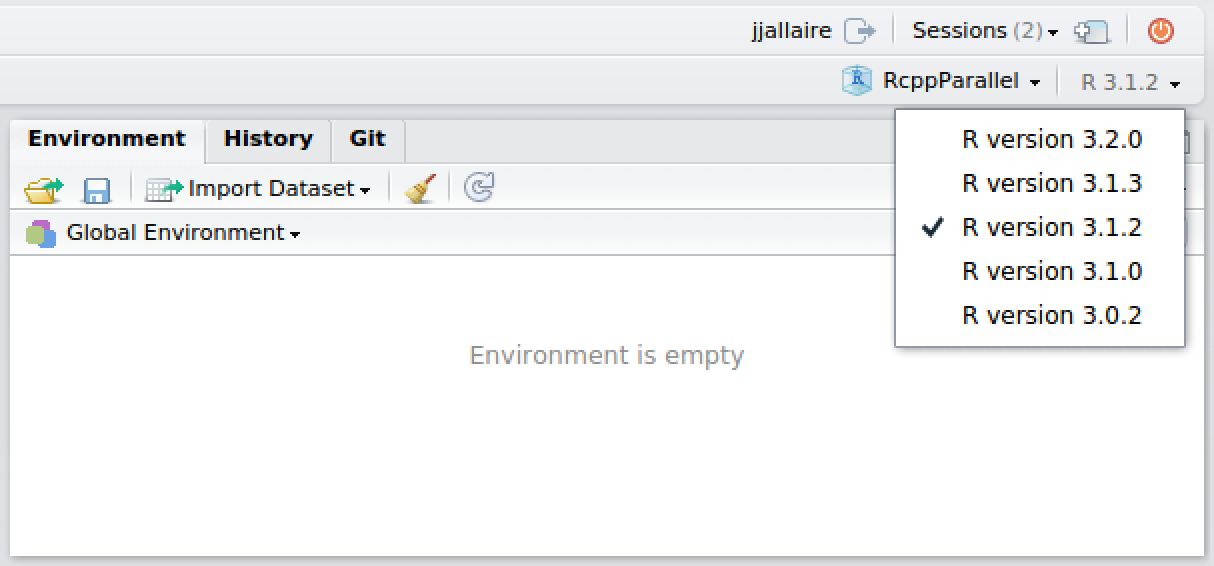
After switching, the specified version will be used for the duration of the current session (see the section on Multiple R Sessions for more details on the lifetime of sessions). Newly created R sessions will continue to use whatever default R version has been configured for the user.
Preserving Versions for Projects
It’s often useful to preserve the version used within an R project irrespective of whatever the current default R version is for a user. This is in fact the behavior by default for RStudio projects however can be changed from the General pane of the Global Options dialog.
This configuration enables users to easily migrate projects one-by-one to a new version of R after it’s been confirmed that all the code continues to work as expected under the new version.
Disabling Use of Multiple Versions
If you want to prevent users from being able to change R versions entirely you can use the r-versions-multiple option:
# /etc/rstudio/rserver.conf
r-versions-multiple=0You can also configure this on a per-user or per-group basis by specifying the r-versions-multiple option within User and Group Profiles.